In this article, we will learn about the major new features that kotlinx.serialization 1.3 brings for developers to manage JSON parsing more efficiently.
Java IO stream-based JSON serialization
We can now read and write JSON directly to network streams or files.
IO stream serialization is currently available only on the JVM platform and for the JSON format.
API includes two main methods:
- Json.decodeFromStream()
- Json.encodeToStream()
| @Serializable | |
| data class DataModel( // properties ) | |
| @OptIn(ExperimentalSerializationApi::class) | |
| fun main() { | |
| URL("https://api.plos.org/search?q=title:DNA").openStream().use { | |
| val jsonData = Json.decodeFromStream<DataModel>(it) // read JSON from a URL | |
| println(jsonData) | |
| FileOutputStream(File("dataModel.json")).use { // save to a file | |
| Json.encodeToStream(jsonData, it) | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
Java IO stream-based JSON serialization.kt
Property-level control over default value encoding
We can force the library to encode the default values by setting the encodeDefaults property of a Json instance to true:
val format = Json { encodeDefaults = true } // false by default
- In
1.3.0 we can control it at the property level by using the experimental@EncodeDefault annotation. - It has a higher priority level than the
encodeDefaultsproperty.
It has two possible values:
The default value is ALWAYS
- ALWAYS: encodes a property’s default value.
- NEVER: doesn’t
encode the default valueregardless of theJsonconfiguration.
| @OptIn(ExperimentalSerializationApi::class) | |
| @Serializable | |
| data class Expert( | |
| val id: Int, | |
| val name: String, | |
| val category: Category, | |
| val publishedArticles: Int?, | |
| // @EncodeDefault default ALWAYS | |
| @EncodeDefault val recentEventLink: String? = null | |
| ) | |
| enum class Category { | |
| ANDROID, KOTLIN, DART, FLUTTER | |
| } |
Property-level control over default value encoding.kt
Excluding null values from serialization
explicitNulls: Another way to reduce the size of the generatedJSON Stringsis by omittingnullvalues.- It defines whether
null property values should be included in theSerialized JSON String. - It’s
trueby default, so allnullsare stored as the values of their corresponding properties.
| val format = Json { explicitNulls = false } | |
| val flutterExpert = Expert(id = 1, "Nav", Category.FLUTTER, null) | |
| val jsonFlutterExpert = format.encodeToString(flutterExpert) | |
| println("EncodedResult: $jsonFlutterExpert") | |
| println("DecodedResult: ${format.decodeFromString<Expert>(jsonFlutterExpert)}") | |
| /* | |
| EncodedResult: | |
| { | |
| "id":1, | |
| "name":"Nav", | |
| "category":"FLUTTER" | |
| } | |
| DecodedResult: | |
| Expert( | |
| id=1, | |
| name=Nav, | |
| category=FLUTTER, | |
| publishedArticles=null, | |
| recentEventLink=null | |
| ) | |
| */ |
Excluding null values from serialization.kt
- Missing field exception 🥵
To deserialize objects from JSON with omitted nulls, we need to make sure that
Json instancewithexplicitNulls == falseis used.It sets all omitted nullable properties to
nullunless they havedefault values.
- Try to decode a
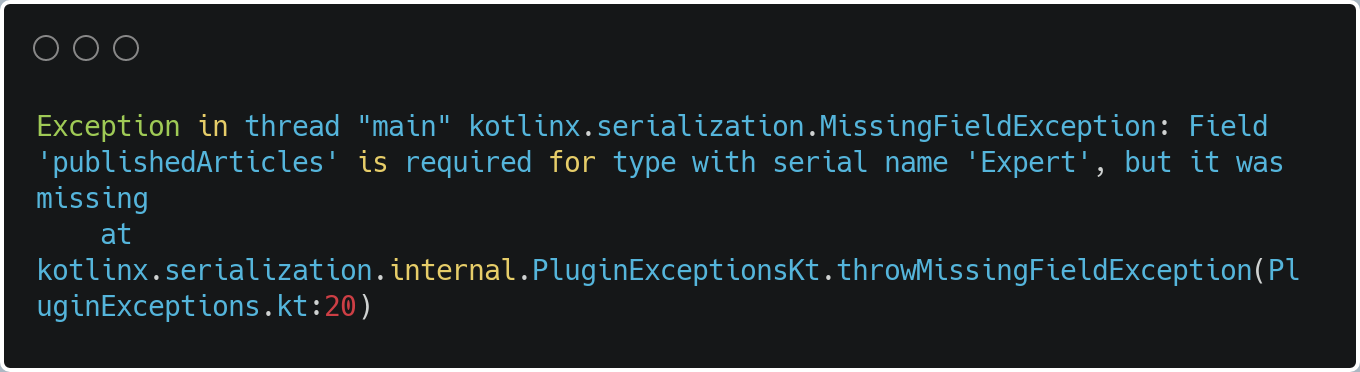
JSON stringwith omitted nulls withexplicitNulls == true(default) it willthrow a MissingFieldException
| val formatExplicitExcludeNullsFalse = Json { explicitNulls = false } | |
| val flutterExpert = Expert(id = 1, "Roman", Category.FLUTTER, null) | |
| val jsonFlutterExpert = formatExplicitExcludeNullsFalse.encodeToString(flutterExpert) | |
| println("Encoded FlutterExpert result: $jsonFlutterExpert") | |
| val formatExplicitExcludeNullsTrue = Json { explicitNulls = true } | |
| println("Decoded FlutterExpert: ${formatExplicitExcludeNullsTrue.decodeFromString<Expert>(jsonFlutterExpert)}") | |
| /* | |
| Exception in thread "main" kotlinx.serialization.MissingFieldException: | |
| Field 'publishedArticles' is required for type with serial name 'Expert', but it was missing | |
| at kotlinx.serialization.internal.PluginExceptionsKt.throwMissingFieldException(PluginExceptions.kt:20) | |
| */ |
Job Offers
Custom polymorphic class discriminators
- In hierarchy serialization, a useful attribute comes into play — class discriminator.
- It stores the exact class of the object that was encoded.
- By default, it has the name
typeand contains a fully qualified class name of theobjectbeingserialized.
In 1.3.0, By using @JsonClassDiscriminator’s
discriminator property we can set a custom discriminator name for each class hierarchy.
| @OptIn(ExperimentalSerializationApi::class) | |
| @Serializable | |
| @JsonClassDiscriminator("languageType") | |
| sealed class Language { | |
| abstract val name: String | |
| } | |
| @Serializable | |
| class Kotlin(override val name: String, private val version: String) : Language() { | |
| fun getFormattedVersion(): String { | |
| return version | |
| } | |
| } | |
| @Serializable | |
| class Java(override val name: String) : Language() | |
| /* | |
| Result: | |
| { | |
| "languageType":"Kotlin", | |
| "name":"Kotlin", | |
| "version":"1.5.30" | |
| } | |
| */ |
 MissingFieldException
MissingFieldException






