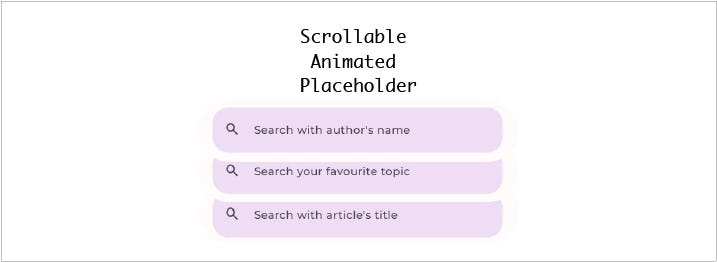
Hello Developers! Today, we will learn to make this appealing scrollable placeholder using Jetpack Compose.
 Scrollable text/hint Demo
Scrollable text/hint Demo
If you are familiar with Jetpack Compose, you would already know that creating animations has been relatively more straightforward. We have access to ‘Ready to use’ functions that can create appealing animation in no time, such as CrossFade, AnimatedVisibility, etc. This type of Composables animates when its target state changes. And by reading this, most of you already guessed how I created this Scrollable animation. Let’s dive into making this animation using a similar Composable function, AnimatedContent.
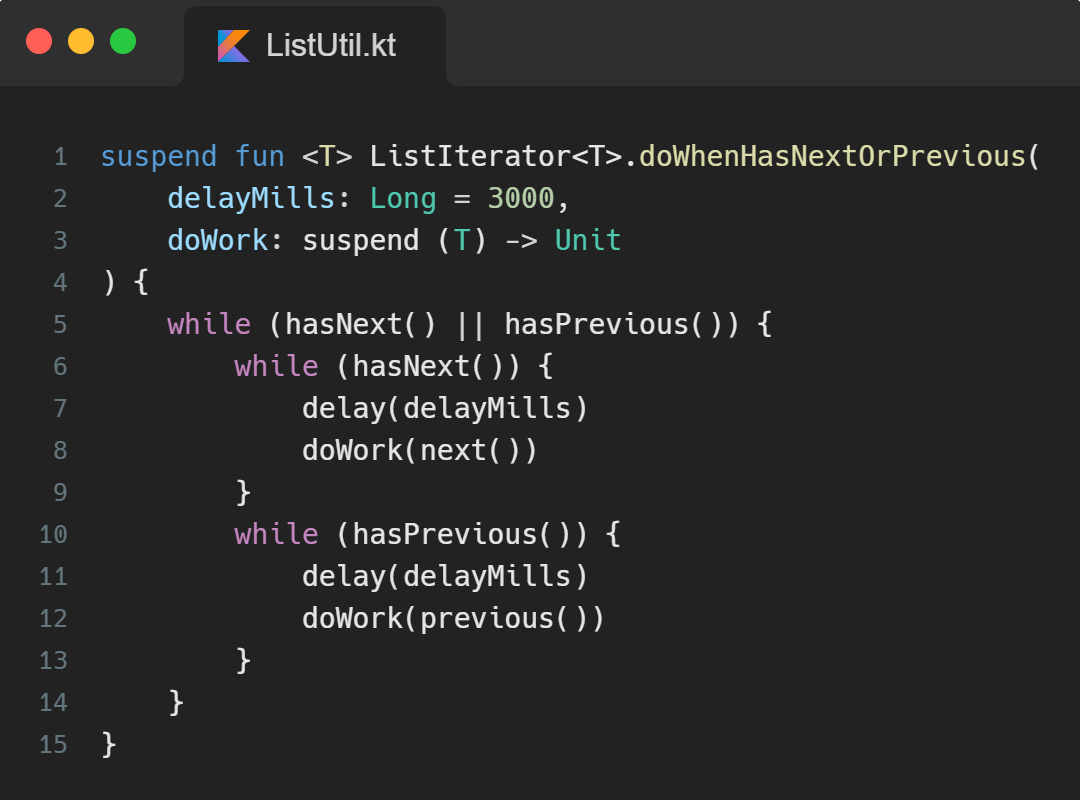
Step 1: Figuring how to loop a value from a list infinitely.
So the idea is that we would be passing a list of Strings to our function, and it should keep looping through them, from 0 to 1, and then restarting again.
You may know about the List Iterator (An iterator over a collection that supports indexed access). We will be using it to check if our list contains any subsequent or previous elements. And Voila! we figured out how to infinitely loop through the values from our list.
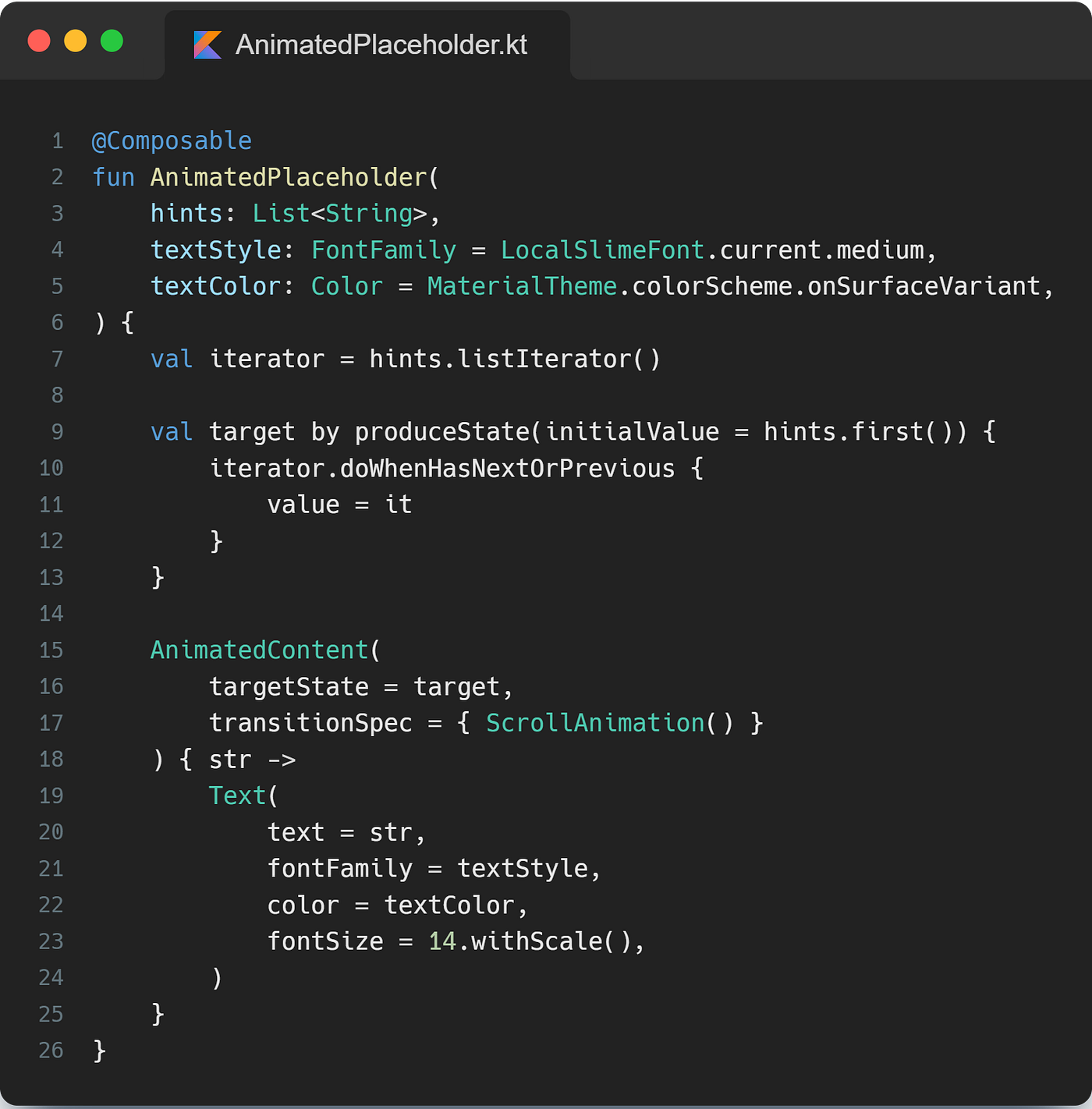
The below function is self-explanatory and is quite helpful.
Special thanks to Doris Liu for helping me fix this code. The 5th line, i.e., which checks for both conditions, I was missing it and wondering why my code isn’t working 😅. Make sure to follow Doris Liu on Twitter for awesome Jetpack Compose animation content.
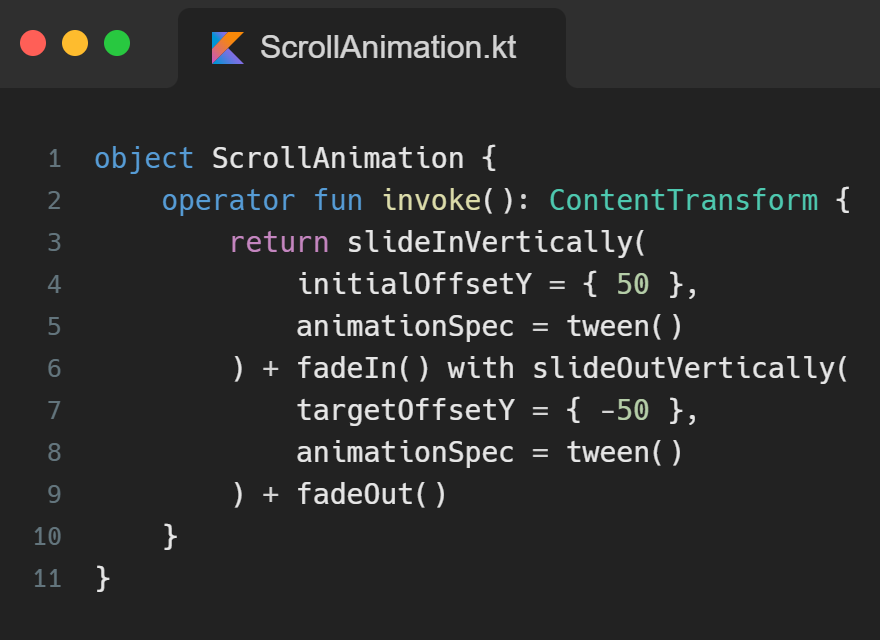
Step 2: Creating the scroll animation
Combining two different animations has never been so effortless. With Jetpack Compose, we can use the operator + to do so.
Here, the scroll animation is nothing but a view that slidesInVertically from the top of our layout. with is a useful extension function from the compose animation library that has EnterTransition as its receiver, and it takes in ExitTransition as a parameter to the function. It is an infix function that can make the code look more readable without us having to write ourEnterTransition.with(ourExitTransition).
The infix keyword according to the official documentation is described as omitting the dot and the parentheses for the call.
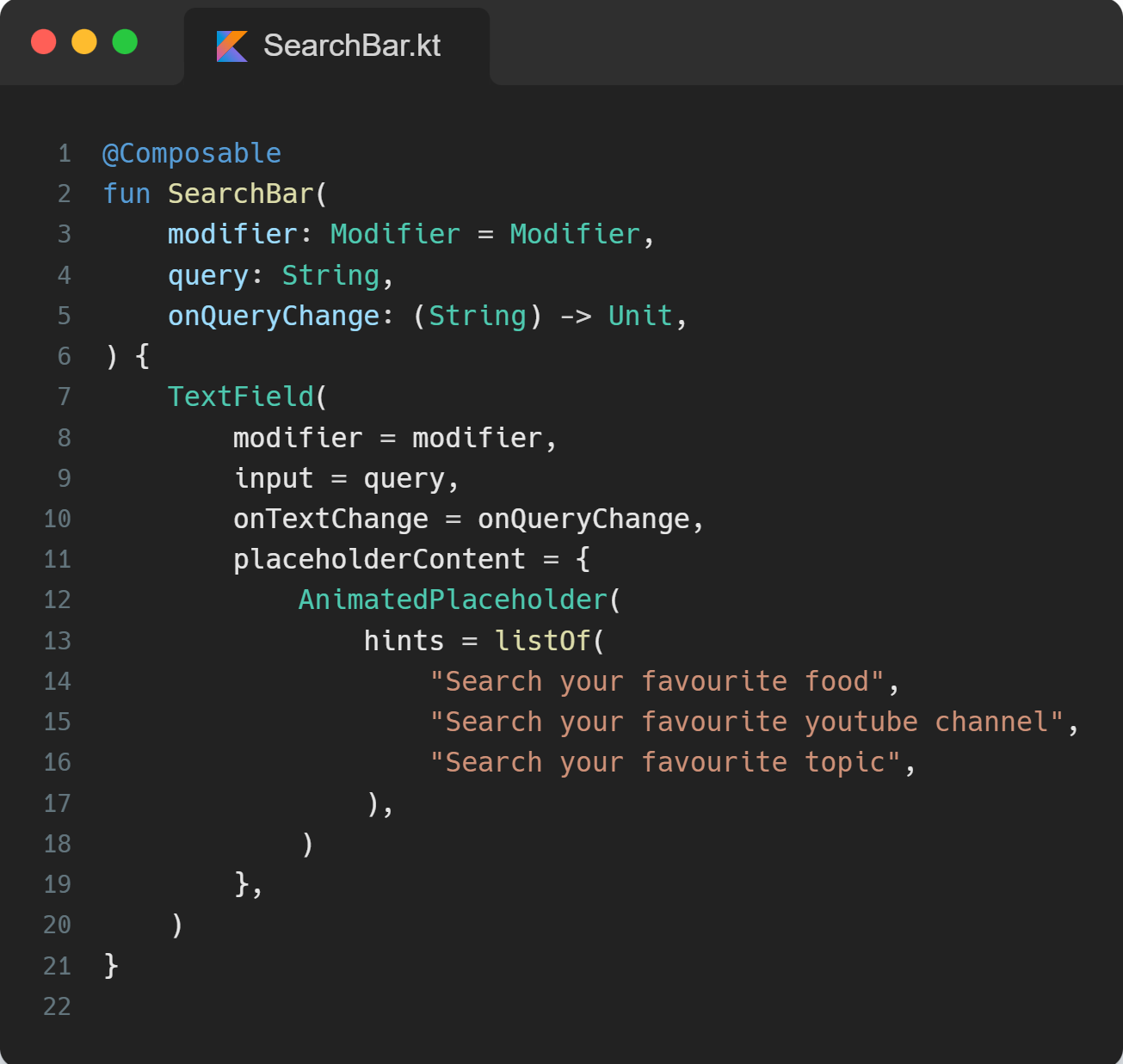
Step 3: Putting the pieces together
As we need to iterate through the values of our list, we access the listIterator from our hints list, and we will further use it to access our extension function, doWhenHasNextOrPrevious.
The AnimatedContent will reanimate when it’s target state changes, i.e. when new item is retrieved from looping through our list, the scroll animation will get triggered again and that is the expected behavior.
We are also using produceState , it converts non-Compose state into Compose state. You can learn more about it here. The initial value of our state would be the first placeholder string in our list, and after that, we would use our extension function doWhenHasNextOrPrevious and assign the received placeholder string from the lambda block as the value of the produceState.
We further pass the newly created variable, target, as targetState of our Animated Content, so as soon as the target variable gets updated with the new value, our animation will retrigger. Finally, for the transactionSpec don’t forget to pass our ScrollAnimation; it is the heart of our animation.
We can also access the value of our target state in theAnimatedContentlambda block.
Job Offers
That’s it. We have successfully implemented Animated Placeholder. Now it’s ready to be used in your Compose TextField.
🙋♂️ If you have any queries, feel free to reach me on Twitter. I would be more than happy to help you!
👍 A clap for this article would be animating. Thank You!
Special thanks to Gabor Varadi for proofreading this article, make sure to follow him on Twitter.
This article was originally published on proandroiddev.com on April 14, 2022