In this article we’ll be implementing caching and pagination with Paging 3. We’ll use Jetpack Compose but you can also follow this article and learn from it even if you are not going to use Jetpack Compose. Except the UI layer, most of it will be similar.
Table of Contents
- Getting Started
- API Endpoint & Creating Models
- Room & Retrofit Setup
- Remote Mediator
- Pager
- UI Layer
– List Setup
– Loading and Error Handling
Prerequisites
We’ll use Room, Retrofit and Hilt in this article, so it’s better you know how they work.
I’ll also assume that you know the basics of how Paging 3 works. If you don’t, I recommend you check this article before this.
Getting Started
App level build.gradle file,
//Paging 3 def paging_version = "3.1.1" implementation "androidx.paging:paging-runtime:$paging_version" implementation "androidx.paging:paging-compose:1.0.0-alpha17" //Retrofit def retrofit_version = "2.9.0" implementation "com.squareup.retrofit2:retrofit:$retrofit_version" implementation "com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-gson:$retrofit_version" //Hilt def hilt_version = "2.44" implementation "com.google.dagger:hilt-android:$hilt_version" kapt "com.google.dagger:hilt-compiler:$hilt_version" implementation "androidx.hilt:hilt-navigation-compose:1.0.0" //Room def room_version = "2.4.3" implementation "androidx.room:room-runtime:$room_version" kapt "androidx.room:room-compiler:$room_version" implementation "androidx.room:room-ktx:$room_version" implementation "androidx.room:room-paging:$room_version" //Coil implementation "io.coil-kt:coil-compose:2.2.2"
Don’t forget to add Internet permission in AndroidManifest.xml,
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
API Endpoint & Creating Models
We’re going to use TheMovieDB API version 3. You can register and get your API key from this link. We will use /movie/popular endpoint.
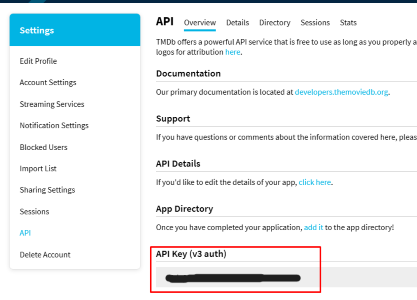
API Key
Response models,
Please put them into different files. I’ve put them into one code block to make it easier to read.
data class MovieResponse(
val page: Int,
@SerializedName(value = "results")
val movies: List<Movie>,
@SerializedName("total_pages")
val totalPages: Int,
@SerializedName("total_results")
val totalResults: Int
)
@Entity(tableName = "movies")
data class Movie(
@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = false)
val id: Int,
@ColumnInfo(name = "original_title")
@SerializedName("original_title")
val ogTitle: String,
@ColumnInfo(name = "overview")
val overview: String,
@ColumnInfo(name = "popularity")
val popularity: Double,
@ColumnInfo(name = "poster_path")
@SerializedName("poster_path")
val posterPath: String?,
@ColumnInfo(name = "release_date")
@SerializedName("release_date")
val releaseDate: String,
@ColumnInfo(name = "title")
val title: String,
@ColumnInfo(name = "page")
var page: Int,
)
That’s it for this part.
Room & Retrofit Setup
Let’s start by creating and implementing Retrofit. API service will be very simple since we are going to use only 1 endpoint.
interface MoviesApiService {
@GET("movie/popular?api_key=${MOVIE_API_KEY}&language=en-US")
suspend fun getPopularMovies(
@Query("page") page: Int
): MovieResponse
}
API service is ready, we’ll create Retrofit instance at the end of this part after finishing Room implementation.
That’s it for Retrofit, now we can implement Room. Before we start, we’ll need to create a new model for caching.
@Entity(tableName = "remote_key")
data class RemoteKeys(
@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = false)
@ColumnInfo(name = "movie_id")
val movieID: Int,
val prevKey: Int?,
val currentPage: Int,
val nextKey: Int?,
@ColumnInfo(name = "created_at")
val createdAt: Long = System.currentTimeMillis()
)
When remote keys are not directly associated with list items, it is best to store them in a separate table in the local database. While this can be done in the
Movietable, creating a new table for the next and previous remote keys associated with aMovieallows us to have a better separation of concerns.
This model is necessary to keep track of pagination. When we get the last item loaded from the PagingState, there’s no way to know the index of the page it belonged to. To solve this problem, we added another table that stores the next, current and previous page keys for each Movie. Keys are page numbers. createdAt is necessary for cache timeout. If you don’t need to check when was the last time we’ve cached the data, you can remove it.
Now we can create Dao for both Movie and RemoteKeys,
@Dao
interface MoviesDao {
@Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE)
suspend fun insertAll(movies: List<Movie>)
@Query("Select * From movies Order By page")
fun getMovies(): PagingSource<Int, Movie>
@Query("Delete From movies")
suspend fun clearAllMovies()
}
@Dao
interface RemoteKeysDao {
@Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE)
suspend fun insertAll(remoteKey: List<RemoteKeys>)
@Query("Select * From remote_key Where movie_id = :id")
suspend fun getRemoteKeyByMovieID(id: Int): RemoteKeys?
@Query("Delete From remote_key")
suspend fun clearRemoteKeys()
@Query("Select created_at From remote_key Order By created_at DESC LIMIT 1")
suspend fun getCreationTime(): Long?
}
Finally, we need to create Database class.
@Database(
entities = [Movie::class, RemoteKeys::class],
version = 1,
)
abstract class MoviesDatabase: RoomDatabase() {
abstract fun getMoviesDao(): MoviesDao
abstract fun getRemoteKeysDao(): RemoteKeysDao
}
That’s it. Now let’s create Retrofit & Room instances.
@Module
@InstallIn(SingletonComponent::class)
class SingletonModule {
@Singleton
@Provides
fun provideRetrofitInstance(): MoviesApiService =
Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl("https://api.themoviedb.org/3/")
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())
.build()
.create(MoviesApiService::class.java)
@Singleton
@Provides
fun provideMovieDatabase(@ApplicationContext context: Context): MoviesDatabase =
Room
.databaseBuilder(context, MoviesDatabase::class.java, "movies_database")
.build()
@Singleton
@Provides
fun provideMoviesDao(moviesDatabase: MoviesDatabase): MoviesDao = moviesDatabase.getMoviesDao()
@Singleton
@Provides
fun provideRemoteKeysDao(moviesDatabase: MoviesDatabase): RemoteKeysDao = moviesDatabase.getRemoteKeysDao()
}
Remote Mediator
Before we start implementing, let’s try to understand what Remote Mediator is and why do we need it.
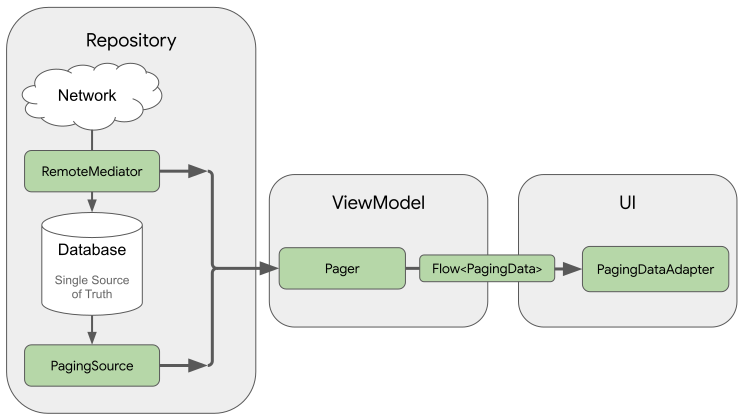
Remote Mediator acts as a signal from the Paging library when the app has run out of cached data. You can use this signal to load additional data from the network and store it in the local database, where a PagingSource can load it and provide it to the UI to display.
When additional data is needed, the Paging library calls the load() method from the Remote Mediator implementation. This function typically fetches the new data from a network source and saves it to local storage.
A Remote Mediator implementation helps load paged data from the network into the database but doesn’t load data directly into the UI. Instead, the app uses the database as the source of truth. In other words, the app only displays data that has been cached in the database.
Now, we can start implementing Remote Mediator. Let’s implement part by part. First, we’ll implement load method.
@OptIn(ExperimentalPagingApi::class)
class MoviesRemoteMediator (
private val moviesApiService: MoviesApiService,
private val moviesDatabase: MoviesDatabase,
): RemoteMediator<Int, Movie>() {
override suspend fun load(
loadType: LoadType,
state: PagingState<Int, Movie>
): MediatorResult {
val page: Int = when (loadType) {
LoadType.REFRESH -> {
//...
}
LoadType.PREPEND -> {
//...
}
LoadType.APPEND -> {
//...
}
}
try {
val apiResponse = moviesApiService.getPopularMovies(page = page)
val movies = apiResponse.movies
val endOfPaginationReached = movies.isEmpty()
moviesDatabase.withTransaction {
if (loadType == LoadType.REFRESH) {
moviesDatabase.getRemoteKeysDao().clearRemoteKeys()
moviesDatabase.getMoviesDao().clearAllMovies()
}
val prevKey = if (page > 1) page - 1 else null
val nextKey = if (endOfPaginationReached) null else page + 1
val remoteKeys = movies.map {
RemoteKeys(movieID = it.id, prevKey = prevKey, currentPage = page, nextKey = nextKey)
}
moviesDatabase.getRemoteKeysDao().insertAll(remoteKeys)
moviesDatabase.getMoviesDao().insertAll(movies.onEachIndexed { _, movie -> movie.page = page })
}
return MediatorResult.Success(endOfPaginationReached = endOfPaginationReached)
} catch (error: IOException) {
return MediatorResult.Error(error)
} catch (error: HttpException) {
return MediatorResult.Error(error)
}
}
}
Job Offers
stateparameter gives us information about the pages that were loaded before, the most recently accessed index in the list, and thePagingConfigwe defined when initializing the paging stream.
loadTypetells us whether we need to load data at the end (LoadType.APPEND) or at the beginning of the data (LoadType.PREPEND) that we previously loaded,
or if this the first time we’re loading data (LoadType.REFRESH).
We’ll implement page attribute later, so let’s start with try/catch block. First, we make API request and get movies and set endOfPaginationReach to movies.isEmpty. If there is no item left to load, we assume it’s exhausted.
Then we start database transaction. Inside of it, we check If loadType is REFRESH and we delete caches. After that, we create RemoteKeys by mapping movies and extract movie.id. Finally, we cache all retrieved movies and remoteKeys.
Now, let’s check how we retrieve page number with RemoteKeys,
@OptIn(ExperimentalPagingApi::class)
class MoviesRemoteMediator (
private val moviesApiService: MoviesApiService,
private val moviesDatabase: MoviesDatabase,
): RemoteMediator<Int, Movie>() {
override suspend fun load(
loadType: LoadType,
state: PagingState<Int, Movie>
): MediatorResult {
val page: Int = when (loadType) {
LoadType.REFRESH -> {
val remoteKeys = getRemoteKeyClosestToCurrentPosition(state)
remoteKeys?.nextKey?.minus(1) ?: 1
}
LoadType.PREPEND -> {
val remoteKeys = getRemoteKeyForFirstItem(state)
val prevKey = remoteKeys?.prevKey
prevKey ?: return MediatorResult.Success(endOfPaginationReached = remoteKeys != null)
}
LoadType.APPEND -> {
val remoteKeys = getRemoteKeyForLastItem(state)
val nextKey = remoteKeys?.nextKey
nextKey ?: return MediatorResult.Success(endOfPaginationReached = remoteKeys != null)
}
}
try {
//Previously implemented
} //...
}
private suspend fun getRemoteKeyClosestToCurrentPosition(state: PagingState<Int, Movie>): RemoteKeys? {
return state.anchorPosition?.let { position ->
state.closestItemToPosition(position)?.id?.let { id ->
moviesDatabase.getRemoteKeysDao().getRemoteKeyByMovieID(id)
}
}
}
private suspend fun getRemoteKeyForFirstItem(state: PagingState<Int, Movie>): RemoteKeys? {
return state.pages.firstOrNull {
it.data.isNotEmpty()
}?.data?.firstOrNull()?.let { movie ->
moviesDatabase.getRemoteKeysDao().getRemoteKeyByMovieID(movie.id)
}
}
private suspend fun getRemoteKeyForLastItem(state: PagingState<Int, Movie>): RemoteKeys? {
return state.pages.lastOrNull {
it.data.isNotEmpty()
}?.data?.lastOrNull()?.let { movie ->
moviesDatabase.getRemoteKeysDao().getRemoteKeyByMovieID(movie.id)
}
}
}
LoadType.REFRESH, gets called when it’s the first time we’re loading data, or when refresh() is called.
LoadType.PREPEND, when we need to load data at the beginning of the currently loaded data set, the load parameter is LoadType.PREPEND.
LoadType.APPEND, when we need to load data at the end of the currently loaded data set, the load parameter is LoadType.APPEND.
getRemoteKeyClosestToCurrentPosition, based on anchorPosition from the state, we can get the closest Movie item to that position by calling closestItemToPosition and retrieve RemoteKeys from database. If RemoteKeys is null, we return the first page number which is 1 in our example.
getRemoteKeyForFirstItem, we get the first Movie item loaded from the database.
getRemoteKeyForLastItem, we get the last Movie item loaded from the database.
Finally, let’s implement caching timeout,
@OptIn(ExperimentalPagingApi::class)
class MoviesRemoteMediator (
private val moviesApiService: MoviesApiService,
private val moviesDatabase: MoviesDatabase,
): RemoteMediator<Int, Movie>() {
override suspend fun initialize(): InitializeAction {
val cacheTimeout = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.convert(1, TimeUnit.HOURS)
return if (System.currentTimeMillis() - (moviesDatabase.getRemoteKeysDao().getCreationTime() ?: 0) < cacheTimeout) {
InitializeAction.SKIP_INITIAL_REFRESH
} else {
InitializeAction.LAUNCH_INITIAL_REFRESH
}
}
//...
}
initializethis method is to check whether cached data is out of date and decide whether to trigger a remote refresh. This method runs before any loading is performed, so you can manipulate the database (for example, to clear old data) before triggering any local or remote loads.
In cases where the local data needs to be fully refreshed, initialize should return LAUNCH_INITIAL_REFRESH. This causes the Remote Mediator to perform a remote refresh to fully reload the data.
In cases where the local data doesn’t need to be refreshed, initialize should return SKIP_INITIAL_REFRESH. This causes the Remote Mediator to skip the remote refresh and load the cached data.
In our example, we’ve set the timeout to 1 hour and retrieve cache time from RemoteKeys database.
That’s it. You can find the RemoteMediator code here, also you can find the full code at the end of this article.
Pager
This is going to be a simple one,
const val PAGE_SIZE = 20
@HiltViewModel
class MoviesViewModel @Inject constructor(
private val moviesApiService: MoviesApiService,
private val moviesDatabase: MoviesDatabase,
): ViewModel() {
@OptIn(ExperimentalPagingApi::class)
fun getPopularMovies(): Flow<PagingData<Movie>> =
Pager(
config = PagingConfig(
pageSize = PAGE_SIZE,
prefetchDistance = 10,
initialLoadSize = PAGE_SIZE,
),
pagingSourceFactory = {
moviesDatabase.getMoviesDao().getMovies()
},
remoteMediator = MoviesRemoteMediator(
moviesApiService,
moviesDatabase,
)
).flow
}
This is similar to creating a
Pagerfrom a simple network data source, but there are two things you must do differently:Instead of passing a
PagingSourceconstructor directly, you must provide the query method that returns aPagingSourceobject from the DAO.You must provide an instance of your
RemoteMediatorimplementation as theremoteMediatorparameter.
The pagingSourceFactory lambda should always return a brand new PagingSource when invoked as PagingSource instances are not reusable.
Finally, we can start implementing UI Layer.
UI Layer
List Setup
List implementation will be very simple,
@Composable
fun MainScreen() {
val moviesViewModel = hiltViewModel<MoviesViewModel>()
val movies = moviesViewModel.getPopularMovies().collectAsLazyPagingItems()
LazyColumn {
items(
items = movies
) { movie ->
movie?.let {
Row(
horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.Center,
verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically,
) {
if (movie.posterPath != null) {
var isImageLoading by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
val painter = rememberAsyncImagePainter(
model = "https://image.tmdb.org/t/p/w154" + movie.posterPath,
)
isImageLoading = when(painter.state) {
is AsyncImagePainter.State.Loading -> true
else -> false
}
Box (
contentAlignment = Alignment.Center
) {
Image(
modifier = Modifier
.padding(horizontal = 6.dp, vertical = 3.dp)
.height(115.dp)
.width(77.dp)
.clip(RoundedCornerShape(8.dp)),
painter = painter,
contentDescription = "Poster Image",
contentScale = ContentScale.FillBounds,
)
if (isImageLoading) {
CircularProgressIndicator(
modifier = Modifier
.padding(horizontal = 6.dp, vertical = 3.dp),
color = MaterialTheme.colors.primary,
)
}
}
}
Text(
modifier = Modifier
.padding(vertical = 18.dp, horizontal = 8.dp),
text = it.title
)
}
Divider()
}
}
}
}
For detailed explanation of list implementation, you can check this link.
List UI
Loading and Error Handling
@Composable
fun MainScreen() {
val moviesViewModel = hiltViewModel<MoviesViewModel>()
val movies = moviesViewModel.getPopularMovies().collectAsLazyPagingItems()
LazyColumn {
//... Movie items
val loadState = movies.loadState.mediator
item {
if (loadState?.refresh == LoadState.Loading) {
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillParentMaxSize(),
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally,
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.Center,
) {
Text(
modifier = Modifier
.padding(8.dp),
text = "Refresh Loading"
)
CircularProgressIndicator(color = MaterialTheme.colors.primary)
}
}
if (loadState?.append == LoadState.Loading) {
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(16.dp),
contentAlignment = Alignment.Center,
) {
CircularProgressIndicator(color = MaterialTheme.colors.primary)
}
}
if (loadState?.refresh is LoadState.Error || loadState?.append is LoadState.Error) {
val isPaginatingError = (loadState.append is LoadState.Error) || movies.itemCount > 1
val error = if (loadState.append is LoadState.Error)
(loadState.append as LoadState.Error).error
else
(loadState.refresh as LoadState.Error).error
val modifier = if (isPaginatingError) {
Modifier.padding(8.dp)
} else {
Modifier.fillParentMaxSize()
}
Column(
modifier = modifier,
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.Center,
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally,
) {
if (!isPaginatingError) {
Icon(
modifier = Modifier
.size(64.dp),
imageVector = Icons.Rounded.Warning, contentDescription = null
)
}
Text(
modifier = Modifier
.padding(8.dp),
text = error.message ?: error.toString(),
textAlign = TextAlign.Center,
)
Button(
onClick = {
movies.refresh()
},
content = {
Text(text = "Refresh")
},
colors = ButtonDefaults.buttonColors(
backgroundColor = MaterialTheme.colors.primary,
contentColor = Color.White,
)
)
}
}
}
}
}
Since we are using Remote Mediator, we’ll use loadState.mediator. We’ll only check refresh and append,
When refresh is LoadState.Loading we’ll show loading screen.

refresh Loading State
When append is LoadState.Loading we’ll show pagination loading.
append Loading
For errors, we check if either refresh or append is LoadState.Error. If we got error on refresh that means, we got an error on initial fetch and we’ll show error screen. If we got error on append that means, we got an error while paginating and we’ll show error at the end of the list.
Let’s see the final result.
That’s it! I hope it was useful. 👋👋
Full Code
MrNtlu/JetpackCompose-PaginationCaching (github.com)
Sources:
This article was originally published on proandroiddev.com on December 22, 2022









